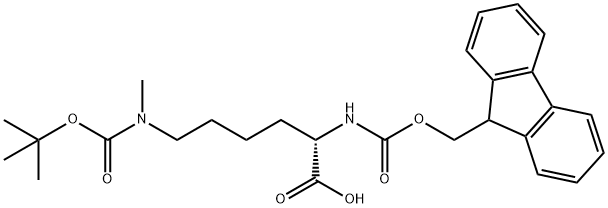
| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
FMOC-LYS(BOC)(ME)-OH | [CAS]
951695-85-5 | [Synonyms]
FMOC-LYS(ME,BOC)-OH
FMOC-LYS(BOC)(ME)-OH
FMOC-L-LYS(BOC, ME)-OH
FMOC-LYSINE(BOC)(ME)-OH
Fmoc-Lys(Me,Boc)-OH, >=97%
Fmoc-Lys(Me,Boc)-OH Novabiochem
FMoc-N-epsilon-Methyl-N-epsilon-t-Boc-L-lysine
Nalpha-Fmoc-Nepsilon-methyl-Nepsilon-Boc-L-lysine
N-ALPHA-FMOC-N-EPSILON,EPSILON-T-BOC-METHYL-L-LYSINE
N-ALPHA-FMOC-N-EPSILON-METHYL-N-EPSILON-T-BOC-L-LYSINE
N-ALPHA-(9-FLUORENYLMETHOXYCARBONYL)-N-EPSILON-T-BUTOXYCARBONYL-N-EPSILON-METHYL-L-LYSINE
N'-[(1,1-Dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-N-[(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-N'-methyl-L-lysine
N-ALPHA-(9-FLUORENYLMETHYLOXYCARBONYL)-N-EPSILON-T-BUTYL-OXYCARBONYL-N-EPSILON-METHYL-L-LYSINE
N-ALPHA-(9-FLUORENYLMETHYLOXYCARBONYL)-N-EPSILON-TERT-BUTYLOXYCARBONYL-N-EPSILON-METHYL-L-LYSINE
(S)-1-(9H-fluoren-9-yl)-10,13,13-trimethyl-3,11-dioxo-2,12-dioxa-4,10-diazatetradecane-5-carboxylic acid | [Molecular Formula]
C27H34N2O6 | [MDL Number]
MFCD01861332 | [MOL File]
951695-85-5.mol | [Molecular Weight]
482.57 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
85-87℃ | [Boiling point ]
665.4±55.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.200 | [storage temp. ]
-15°C | [solubility ]
Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | [form ]
Powder | [pka]
3.88±0.21(Predicted) | [color ]
White to off-white | [Optical Rotation]
-4°(C=0.01g/ml MEOH) | [InChIKey]
JHMSFOFHTAYQLS-QHCPKHFHSA-N | [SMILES]
C(O)(=O)[C@H](CCCCN(C(OC(C)(C)C)=O)C)NC(OCC1C2=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C=CC=C2)=O |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Fmoc-lys (BOC) (ME)-OH is a kind of protected form of lysine. Lysine is double-protected by butyloxycarbonyl (BOC) and 9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbon (FMOC). It is a derivative for the introduction of monomethyl-lysine during Fmoc SPPS. Coupling can be carried out using any standard activation method. The Boc protecting group can be removed through the TFA-mediated cleavage reaction. As a kind of protected amino acid, it is an important intermediate in various fields such as peptide synthesis, asymmetric synthesis, medicinal chemistry as well as polymer chemistry.
| [General Description]
Fmoc protected N-methylated lysine | [reaction suitability]
reaction type: Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis | [Synthesis]
The general procedure for the synthesis of N2-(((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonyl)-N6-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-N6-methyl-L-lysine from di-tert-butyl dicarbonate and (S)-2-((((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonyl)amino)-6-(methylamino)hexanoic acid was performed as follows: the light yellow solid crude product was dissolved in water (500 mL) and THF (500 mL) in a 1:1 solvent mixture, sodium bicarbonate (63 g, 0.75 mol) was added, and the solution was stirred until clarified. Subsequently, Boc2O (142 g, 0.65 mol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (200 mL), added to the reaction system and reacted for 4.0 h at room temperature. Complete reaction of the feedstock was confirmed by HPLC monitoring. After completion of the reaction, the reaction solution was neutralized with dilute hydrochloric acid to pH 5-6. The organic solvent was removed by concentration under reduced pressure and the aqueous phase was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic phase was washed with saturated brine and concentrated to give a white solid product (235 g). This white solid was further purified by recrystallization from ethyl acetate and n-hexane, resulting in 224 g of white solid powder in 93% yield and 99.8% purity. |
| Questions and Answers (Q&A) | Back Directory | [Uses]
- Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) depends on trimethylation of H3 Lys 9; aggregation of chromatines depends on Lys methylation
- Fmoc-Lys(Boc, Me)-OH is useful for preparing monomethylated histone fragments utilized in studying the regulatory roles of methylated histones. Fmoc-Lys(Boc,Me)-OH can be coupled using standard activating procedures. The Boc group on the side epsilon nitrogen atom is removed with TFA, usually at the same time as the peptide is cleaved from the resin.
- Fmoc-Lys(Boc, Me)-OH is a novel derivative for the introduction of monomethyl-lysine during Fmoc SPPS. Coupling can be carried out using any standard activation method. Removal of the Boc protecting group occurs during the course of the TFA-mediated cleavage reaction.
| [References]
http://www.chempep.com/ChemPep_Products2_Fmoc-Amino-Acid_Fmoc-Lys_Boc_Me_-OH.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peptide_synthesis
Tung, C. L., et al. "A fluorogenic probe for recognizing 5-hydroxylysine inspired by serine/threonine ligation. " Chemical Communications 50.40(2014):5298-300.
|
|
|