
(-)-DIOP synthesis
- Product Name:(-)-DIOP
- CAS Number:32305-98-9
- Molecular formula:C31H32O2P2
- Molecular Weight:498.54
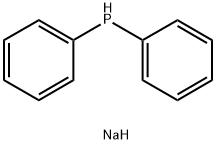
4376-01-6
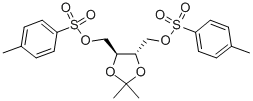
37002-45-2

32305-98-9
In a 250 mL three-necked round-bottomed flask fitted with a PTFE stirrer, a coated stirring bar, a thermometer and its adapter, a reflux condenser with a gas inlet at the top, and a device with a 60 mL dosing funnel and PTFE Claisen fittings were assembled. The sample port of the plug valve was heated using a hot air gun and simultaneously purged with a rapid nitrogen stream to degas. 16.0 g (36.1 mmol) of (-)-1,4-di-O-toluenesulfonyl-2,3-O-isopropylidene-L-threitol (CAS No. 37002-45-2, also known as bis(toluenesulfonate)) was added to the reactor and purged with a nitrogen purge for an additional 30 min. Bis(toluene sulfonate) was dissolved in 100 mL of degassed anhydrous tetrahydrofuran. The sodium diarylphosphide solution prepared in step 2) was transferred to a 60 mL addition funnel through a cannula and added dropwise at a rate to a rapidly stirred solution of bis(toluene sulfonate), keeping the reactor temperature below 40 °C. Upon addition of the electrophilic reagent, the solution was reddish-orange in color and the diaryl phosphide salt disappeared rapidly to form a beige suspension. After dropwise addition, the oil bath was placed below the reactor and heated to 50 °C for 45 min to complete the phosphide coupling step. Subsequently, the Claisen adapter assembly was replaced with a short-range distillation head and approximately 50% of the tetrahydrofuran was removed by distillation. Phase separation was achieved by adding 100 mL of degassed heptane and water. The two-phase solution was filtered through an inert glass sintered funnel to remove carbon black and the lower aqueous phase was removed through a cannula. The upper organic phase was washed with 50 mL of degassed water and the aqueous phase was again removed through a cannula. Next, the organic heptane phase was extracted with 100 mL of anhydrous degassed acetonitrile, the lower acetonitrile phase was removed through a cannula, and the extraction was repeated once more with 50 mL of degassed acetonitrile. The acetonitrile phases were combined and transferred to a single-necked round-bottomed flask with a polytetrafluoroethylene stopcock valve and 24/40 standard conical ground glass fittings. The volatiles were removed on a rotary evaporator to give a viscous orange-brown glassy solid, which was further dried under vacuum. In the drying oven, the plug valve was replaced with a PTFE Claisen adapter with reflux condenser and gas inlet. The glassy solid was dissolved in 100 mL of degassed methanol, introduced via cannula or syringe, and heated to reflux to completely dissolve the ligand. Heating was stopped and the flask was immersed in an ice bath and cooled to -10 °C to give a white to off-white/beige solid. The solid DIOP ligand was collected through a glass sintered Schlenck filter, washed with cooled methanol, and dried overnight under vacuum. A final 11.7 g (23.5 mmol, molecular weight 498.34 g/mol) of (-)-DIOP ligand was obtained. The ligand was analyzed by 1H NMR (CDCl3: δ = 7.58-7.29 ppm, multiple peaks, 20H, aromatic; δ = 4.0-3.8 ppm, double peaks, 2H, -CH-; δ = 2.50-2.25 ppm, multiple peaks, 4H, -CH2-; δ = 1.35 ppm, single peaks, 6H, -CH3), 13C NMR (data not shown but consistent with the target product) and 31P NMR (CDCl3: δ=-22.87 ppm, single peak) for characterization. The molar percent P purity was >99%, and the total phosphorus content was determined by ICP to be 12.2 wt% P (theoretical value of 12.4 wt% P), indicating a chemical purity of approximately 98.4%, with a molecular formula of C31H32P2O2 and a molecular weight of 498.34 g/mol.

4376-01-6
3 suppliers
inquiry

37002-45-2
89 suppliers
$33.60/1G

32305-98-9
138 suppliers
$18.00/100mg
Yield:32305-98-9 60.7%
Reaction Conditions:
in tetrahydrofuran;Carnea E-22 at 40 - 50;Product distribution / selectivity;Inert atmosphere;
Steps:
4.A.i
A 250 mL 3 neck round bottom glass reactor equipped with a Teflon coated stir bar, a thermometer and its adapter, a reflux condenser with a gas inlet on top, and a Claisen adapter to which is attached a 60 mL addition funnel and a Teflon stopcock sample port is heated with a heat gun while purging with a rapid flow of N2 to degas. The reactor is then charged with 16.0 grams of (-)-1,4-di-O-tosyl-2,3-O-isopropylidene-L-threitol (CASNo. 37002-45-2, 36.1 mmol), aka bis(tosylate) and flushed with N2 purge for an additional 30 minutes. The bis(tosylate) is then dissolved in 100 mL of degassed, anhydrous THF. The sodium diarylphosphide solution prepared in Step 2). A). above is then transferred via cannula to the 60 mL addition funnel in parts and added dropwise to the rapidly stirring bis(tosylate) at rate so as to maintain a reactor temperature below 40° C. Upon addition to the electrophile, the reddish-orange color of the diarylphosphide salt rapidly disappears to give a final suspension with a beige color. After all of the phosphide is added, an oil bath is placed beneath the reactor and the contents heated to 50° C. for 45 minutes to complete phosphide coupling step. The Claisen adapter assembly is then replaced by a short path distillation head and roughly 50% of the THF is removed. Then 100 mL of degassed heptane and water, each, are added to effect a phase split. The biphasic solution is then passed through an inerted glass fritted funnel to remove the carbon black and the lower aqueous phase removed via cannula. The upper organic phase is rinsed with an additional 50 mL of degassed water, again removed via cannula. The organic heptane phase is then extracted with 100 mL of anhydrous, degassed acetonitrile, the lower acetonitrile phase removed via cannula, and again the organic heptane phase is extracted with 50 mL of degassed acetonitrile. The acetonitrile phases are combined and transferred to a 1 neck round bottom flask with a Teflon stopcock on top with a 24/40 standard tapered ground glass joint on top. The volatiles are removed on a rotary evaporator to yield a viscous orange-brown glassy solid that is further dried under vacuum. In a dry box, the Teflon stopcock is replaced with a Claisen adapter to which is attached a reflux condenser with a gas inlet on top and a Teflon stopcock sample port. The glassy solid is then dissolved in crystallized in 100 mL of degassed methanol introduced by cannula or syringe followed by heating to reflux to completely dissolve the ligand. The heat is removed and the DIOP ligand suspension in the flask is immersed in an ice batch and cooled to -10° C. to yield a white to off-white/beige colored solid. The solid DIOP ligand is collected on a glass fritted Schlenck filter, rinsed with chilled methanol, and then dried overnight on the frit under vacuum. A total of 11.7 grams (23.5 mmol, 498.34 g/moll) of the (-)-DIOP ligand was isolated. The ligand is fully characterized by 1H(CDCl3: δ=7.58-7.29 ppm, cm, 20H, aromatic; δ=4.0-3.8 ppm, dd, 2H, -CH-; 6-2.50-2.25 ppm, ddd, 4H, -CH2-; δ1.35 ppm, s, 6H, -CH3) 13C (not reported here, but consistent with desired product), and 31P NMR (CDCl3: δ=-22.87 ppm, singlet, and a mol % P purity>99%) and by ICP for a total phosphorus content of 12.2 wt % P (theory=12.4 wt % P) representing a chemical purity of approximately 98.4% for molecular formula=C31H32P2O2 and molecular weight=498.34 g/mol.
References:
Arkema Inc. US2010/234642, 2010, A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 13

829-85-6
276 suppliers
$33.00/25g

37002-45-2
89 suppliers
$33.60/1G

32305-98-9
138 suppliers
$18.00/100mg

50622-09-8
167 suppliers
$22.00/250mg

32305-98-9
138 suppliers
$18.00/100mg

59779-75-8
38 suppliers
$48.00/1g

32305-98-9
138 suppliers
$18.00/100mg

37002-45-2
89 suppliers
$33.60/1G

32305-98-9
138 suppliers
$18.00/100mg