| Identification | More | [Name]
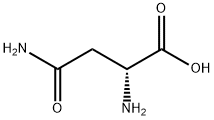
Boc-D-Asparagine | [CAS]
75647-01-7 | [Synonyms]
BOC-D-ASN
BOC-D-ASN-OH
BOC-D-ASPARAGINE
NALPHA-BOC-D-ASPARAGINE
N-ALPHA-T-BOC-D-ASPARAGINE
N-ALPHA-T-BUTOXYCARBONYL-D-ASPARAGINE
N-ALPHA-T-BUTYLOXYCARBONYL-D-ASPARAGINE
NALPHA-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-D-ASPARAGIN
NALPHA-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-D-ASPARAGINE
N-ALPHA-TERT-BUTYLOXYCARBONYL-D-ASPARAGINE
N-BOC-D-ASPARAGINE
T-BUTYLOXYCARBONYL-D-ASPARAGINE
N-BOC-D-Asn-OH
NA-T-BOC-D-ASPARAGINE
N-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-D-asparagine
N2-[(1,1-DIMETHYLETHOXY)CARBONYL]-D-ASPARAGINE
BOC-D-ASPARGINE extrapure | [EINECS(EC#)]
231-405-2 | [Molecular Formula]
C9H16N2O5 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00065558 | [Molecular Weight]
232.23 | [MOL File]
75647-01-7.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white fine crystalline powder | [Melting point ]
165-169 °C
| [alpha ]
9 º (c=1, DMF) | [Boiling point ]
374.39°C (rough estimate) | [density ]
1.2896 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
7.7 ° (C=1, DMF) | [storage temp. ]
Store at 0°C | [solubility ]
soluble in Dimethylformamide | [form ]
Powder | [pka]
3.79±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
White | [BRN ]
4843040 | [CAS DataBase Reference]
75647-01-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
T | [Risk Statements ]
25 | [Safety Statements ]
S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [HS Code ]
29241990 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
white fine crystalline powder | [Uses]
Nα-Boc-D-asparagine is an N-Boc-protected form of D-Asparagine (A788990). D-Asparagine is an isomer of L-Asparagine (A790005) and is used by bacteria (such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae) as a sole nitrogen source for replication. L-Asparagine is also a competitive inhibitor of staphylococcal L-asparaginase and is used as a reagent to synthesize peptide antibiotics. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Boc-D-asparagine is an asparagine derivative. | [reaction suitability]
reaction type: Boc solid-phase peptide synthesis | [Synthesis]
General procedure for the synthesis of BOC-L-asparagine from D-asparagine monohydrate and di-tert-butyl dicarbonate: in Example 75, 5-[5-fluoro-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-indol-(3Z)-ylidene-methylene]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid [(S)-1-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-2,5-dioxo-pyrrolidin- 3-yl]-amide ester (75a, 2.0 g, 15 mmol) and Na2CO3 (1.6 g, 15 mmol) were dissolved in a solvent mixture of H2O/1,4-dioxane (30 mL/30 mL). To this solution, di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Boc)2O (3.96 g, 18.2 mmol) was added dropwise at room temperature. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight and subsequently 1,4-dioxane was removed by evaporation. The remaining aqueous solution was adjusted to pH=2 with 37% HCl. The precipitate precipitated was filtered, washed with water and dried to afford the target product 75b (2.97 g, 84% yield) as a white solid. | [References]
[1] Patent: WO2008/33562, 2008, A2. Location in patent: Page/Page column 86
[2] Patent: US2009/76005, 2009, A1. Location in patent: Page/Page column 44
[3] Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2013, vol. 56, # 7, p. 2936 - 2947
[4] Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, vol. 136, # 26, p. 9244 - 9247 |
|
|